Corneal inflammation includes corneal swelling (a clear, dome-shaped tissue in front of your eyes that covers the pupil and iris) and is one of the most common diseases in the cornea. Corneal inflammation may be associated with infection, or it may not be infectious. Non-infectious inflammation can be caused by relatively minor damage, as a result of the use of contact lenses for a long time or by the collision of the foreign body with the eye. Infectious inflammation can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites.
If you have red eyes or other symptoms of corneal inflammation, see your ophthalmologist. If rapid eye care is performed, diagnosis of the causes of partial to moderate corneal inflammation can usually be achieved without loss of vision. If the disease remains untreated, or if the infection is severe, corneal inflammation can have serious problems and complications and may damage vision.
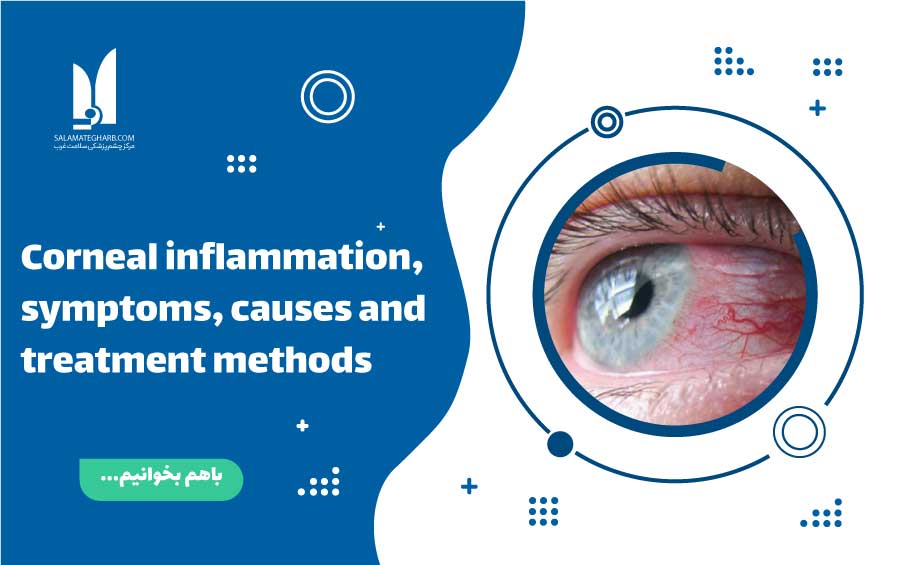
Symptoms of corneal inflammation
Signs and symptoms of corneal inflammation include:
- Red-eye
- Eye pain
- Tearing or secreting other excessive fluids from the eye
- Difficulty opening the eyelids due to pain or irritation
- Blurred vision
- Visual loss
- Sensitivity to light
- The feeling of external jasper in the eye
When to see an ophthalmologist ?
If you notice any signs or symptoms of corneal inflammation, see your doctor. Delays in diagnosis and treatment of corneal inflammation can cause serious complications, even blindness.
Causes of corneal inflammation
The most important causes of corneal inflammation are:
Damage: If any foreign body causes scratches or damage to the cornea surface, non-infectious corneal inflammation may also cause damage to microorganisms to damage the cornea and cause inflammation of the infectious cornea.
Infected contact lenses: Bacteria, fungi or parasites (especially the Acanthamoeba microscopic parasite) may sit on the surface of contact lenses or their frames when contact lenses are in the eye, which may infect the cornea and cause inflammation of the infectious cornea, and excessive use of contact lenses can cause inflammation of the cornea, which can also be infectious.
Viruses: Herpes virus (herpes simplex and herpes zoster) may cause inflammation of the infectious cornea.
Bacteria: Gonorrhea-causing bacteria can cause corneal inflammation.
Contaminated water: Bacteria, fungi, and parasites in the water (especially in oceans, rivers, lakes and tubs) can enter your eye when you swim, causing corneal inflammation, but even if you are exposed to this bacterium, fungus or parasite, a healthy cornea rarely becomes infectious unless there is damage on the surface of the cornea (for example, the use of contact lenses for a long time).

Leave A Comment